The Dell XPS 14 and 16 underwent a complete redesign this year, introducing some controversial changes, such as moving to soldered RAM. This decision has stirred up discussions, especially among fans of the XPS series who valued upgradability in the past.
While Dell is not the first to adopt soldered RAM, it is one of the last major manufacturers to do so. This shift has affected not only productivity laptops but also high-performance gaming laptops like the ROG Zephyrus G14.
To understand why laptop companies are leaning towards soldered RAM, I reached out to industry leaders to explore the reasoning behind this strategic shift.
What is soldered RAM and why does it matter?
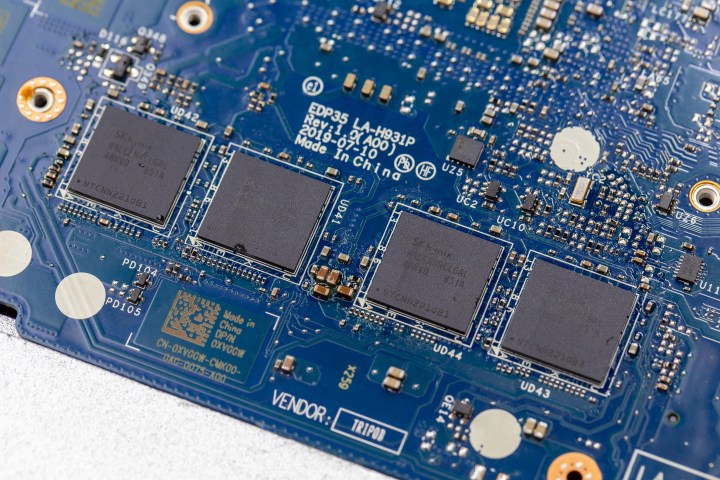
Soldered RAM refers to computer memory that is permanently attached to the motherboard, making it impossible to upgrade or repair. This contrasts with traditional RAM sticks, known as SO-DIMMs, which can be removed and replaced.
While soldered RAM offers space-saving benefits for thin and light laptops, budget models, and high-end gaming machines, it limits future upgradability and repair options. The decision to use soldered RAM is primarily driven by the pursuit of thinner designs, improved battery life, and enhanced cooling performance.

While laptop manufacturers emphasize the benefits of soldered RAM, many end-users, especially power users, are concerned about the limitations it imposes. The lack of upgradability and the complexity of repairs can deter enthusiasts who value customization and longevity in their devices.
Despite the push towards soldered RAM for performance and design reasons, the debate over its impact on end-users’ experience continues to evolve.
What makes soldered RAM popular?
Greg Davill
Haval Othman, senior director of experience engineering at HP, highlighted the advantages of soldered RAM, such as space-saving, power efficiency, and improved form factor. The decision to use soldered RAM is often driven by considerations of thermals, efficiency, and design constraints.
One of the key benefits of soldered RAM is its space-saving capability, enabling manufacturers to create thinner and lighter laptops while maximizing battery life and performance. This trend aligns with the industry’s focus on compact and portable designs for modern laptops.
While soldered RAM offers advantages in terms of space efficiency and manufacturing cost, some users express concerns about its impact on upgradability and repairability. The debate over the pros and cons of soldered RAM continues to shape the laptop market and consumer preferences.


